Powering Up at Home: The Complete Guide to Residential EV Charging Stations
The Surging Demand for Home EV Charging Solutions
Electric vehicles are no longer just a futuristic concept—they're rapidly becoming a mainstream reality. With EV sales reaching an unprecedented 346,309 units in last year's third quarter (nearly 9% of all automotive sales according to Cox Automotive), the need for convenient home charging solutions has never been greater.
While highway infrastructure is expanding thanks to a $5 billion federal allocation for public charging networks, the real convenience comes from being able to power up right in your own garage. Interest in residential charging stations has more than doubled over the past decade, with 49% of new home buyers now expressing interest in this feature compared to just 23% ten years ago, according to the National Association of Home Builders.
Despite this growing demand, only about 25% of builders are including charging stations in their new constructions this year, creating a gap that homeowners often need to address themselves. For existing homeowners, charging stations don't even register on the National Association of Realtors' list of desired features—yet the practical need remains for EV owners.
Understanding Your Home Charging Options
Before diving into installation, it's crucial to understand the three levels of EV charging technology available today:
Level 1 Charging: The Basic Solution
Level 1 chargers represent the entry point for home charging:
- Uses standard 120-volt household outlets
- Typically comes included with most new electric vehicles
- Requires no special installation in most homes
- Adds approximately 4-7 miles of range per hour of charging
- Over a 12-hour overnight charge, provides between 48-84 miles of range
While Level 1 chargers are sufficient for drivers with minimal daily commutes or those who use their EVs primarily for short local trips, they may prove inadequate for high-mileage drivers.
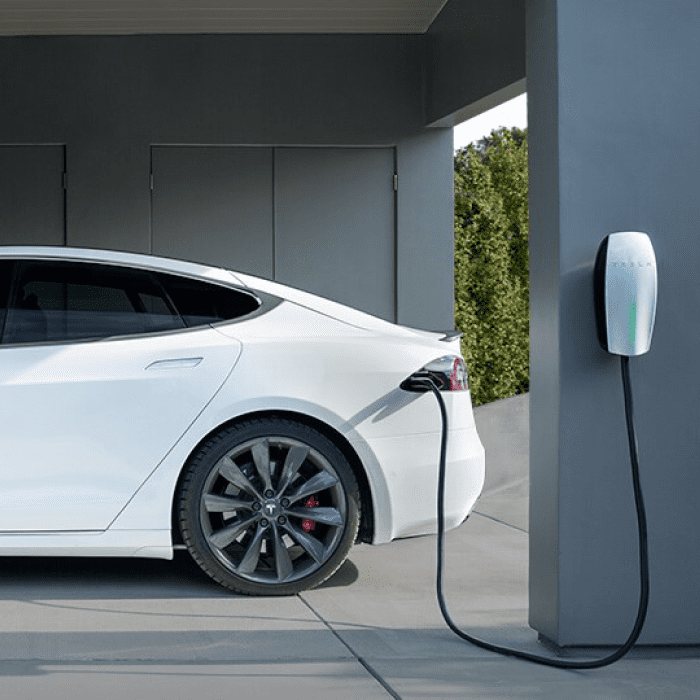
Level 2 Charging: The Sweet Spot for Homeowners
Level 2 charging represents the optimal balance of speed and practicality for most homeowners:
- Operates on a 240-volt circuit (similar to what powers electric dryers and ranges)
- Delivers 20-60 miles of range per hour of charging
- Can fully charge most EVs overnight (240-720 miles in a 12-hour period)
- Requires professional installation and possibly electrical upgrades
- May need permits from local building departments
Popular units like the ChargePoint HomeFlex (compatible with all EVs including Tesla) cost around $549 before installation, though prices vary by manufacturer and model.
Level 3 Charging: Commercial-Grade Power
Level 3 chargers deliver the fastest charging speeds but come with significant limitations for residential use:
- Requires 480-volt service, well beyond typical residential electrical capacity
- Bypasses the vehicle's onboard charging system by converting AC to DC externally
- Demands substantial electrical upgrades, often including additional service panels
- Financially impractical for single-family homes
- Better suited for commercial or multi-family properties
Pre-Installation Considerations for Homeowners
Before purchasing any equipment, several critical steps should be taken:
- HOA Approval: If you live in a community with a homeowners association, check whether EV chargers are permitted under the covenants and restrictions.
- Electrical Assessment: Hire a licensed, insured electrician to evaluate your home's electrical panel capacity. Many older homes will require a "heavy up" upgrade to accommodate a 240-volt circuit for Level 2 charging.
- Installation Location: The distance between your electrical panel and your intended charging location significantly impacts installation costs. Most installations place the charger 15-30 feet from the panel, according to ChargePoint.
- Vehicle Requirements: Some EV manufacturers recommend charging batteries to only 80% capacity rather than 100%, supplementing with regenerative braking. Review your specific vehicle's guidelines before selecting a charging system.
Financial Incentives That Lower Your Costs
Installing a home charging station becomes significantly more affordable when you leverage available incentives:
- Federal Tax Credits: The federal government offers a tax credit worth 30% of charging equipment and installation costs, up to $1,000. This is separate from the up-to-$7,500 tax credit available for purchasing qualifying electric vehicles.
- State Programs: Benefits vary significantly by location. For example, Maryland offers residential rebates covering 50% of costs up to $700 per household.
- Local Incentives: Some municipalities offer their own programs, like Westerville, Ohio's $300 rebate for residents who participate in off-peak charging programs.
- Utility Company Offers: Energy providers increasingly offer EV-specific incentives. Duke Energy in Florida provides a $7.50 monthly credit to customers with Level 2 chargers who charge during off-peak hours, while Jacksonville Electric Authority offers both monthly credits and installation rebates up to $300.
The Economics of Home Charging
While the initial setup costs may seem significant, the long-term economics favor home charging:
- Fuel Savings: EV owners typically save up to $1,000 annually on fuel costs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Increased Electricity Costs: Expect your monthly electricity bill to increase by approximately $60 when regularly charging at home.
- Off-Peak Savings: Scheduling charging during low-demand hours (typically overnight) can significantly reduce the per-kilowatt-hour cost, further improving your savings.
- Home Value: As EV adoption increases, homes with pre-installed charging infrastructure may command premium resale values, though this trend is still emerging.
Insights About Home EV Charging
Do I need to upgrade my home's electrical system to install an EV charger?
Not necessarily. If you're satisfied with a Level 1 charger that uses a standard 120V outlet, no upgrades are typically required. However, for the faster and more practical Level 2 charging, most homes will need a dedicated 240V circuit installed by a licensed electrician. Older homes with lower-capacity electrical panels (100 amps or less) may require a panel upgrade to safely accommodate the additional load.
How much can I really save by charging at home versus using public charging stations?
Substantial savings are possible. Public DC fast chargers typically cost $0.40-$0.60 per kWh, while home electricity rates average around $0.15 per kWh nationally (with significant regional variation). For a vehicle with a 75kWh battery, that's a difference of approximately $19-$34 per full charge. If you charge weekly, annual savings could exceed $1,000 compared to exclusively using premium public charging options.
Will installing a charging station void my home's warranty or insurance?
When properly installed by a licensed electrician with appropriate permits, an EV charging station should not affect your home warranty or insurance. However, it's advisable to inform your insurance provider about the installation, as some companies offer specific coverage or discounts for green home improvements. Improper DIY installations, however, could potentially void electrical system warranties and create insurance complications.
Can I install a charging station in a condo or apartment?
This remains challenging for many multi-unit dwellers. While some newer developments include EV infrastructure, residents of existing buildings typically need approval from landlords, HOAs, or condo boards. Some states have "right to charge" laws that prevent unreasonable restrictions, but installation logistics and shared electricity metering often present significant hurdles. Community advocacy and cost-sharing proposals can sometimes overcome these barriers.